ISO 22007-2, ISO 22007-7, GB/T 32064 (solids)
ASTM D7896 (liquids)
ISO 22007-7:2023
ASTM D5334-22a, ASTM D5930
The powerful combination of Transient Plane Source (TPS, ISO 22007-2) for solids, Transient Hot Wire (THW, ASTM D7896-19) for liquids, Transient Line Source (TLS) and Transient Hot Strip (THS) gives the MP-1 a unique and versatile selection of testing methods for your sample type. The TPS and THW methods are widely used for accurate measurement of absolute thermal conductivity, thermal diffusivity, specific heat and thermal effusivity. This versatility is greatly expanded with the addition of our proprietary Temperature Platform (TP) which is appreciated by academic and commercial users alike.
Following ISO 22007-2 and ASTM 7896-19, the TPS and THW are primary measurement methods trusted worldwide with 1000s of published papers.
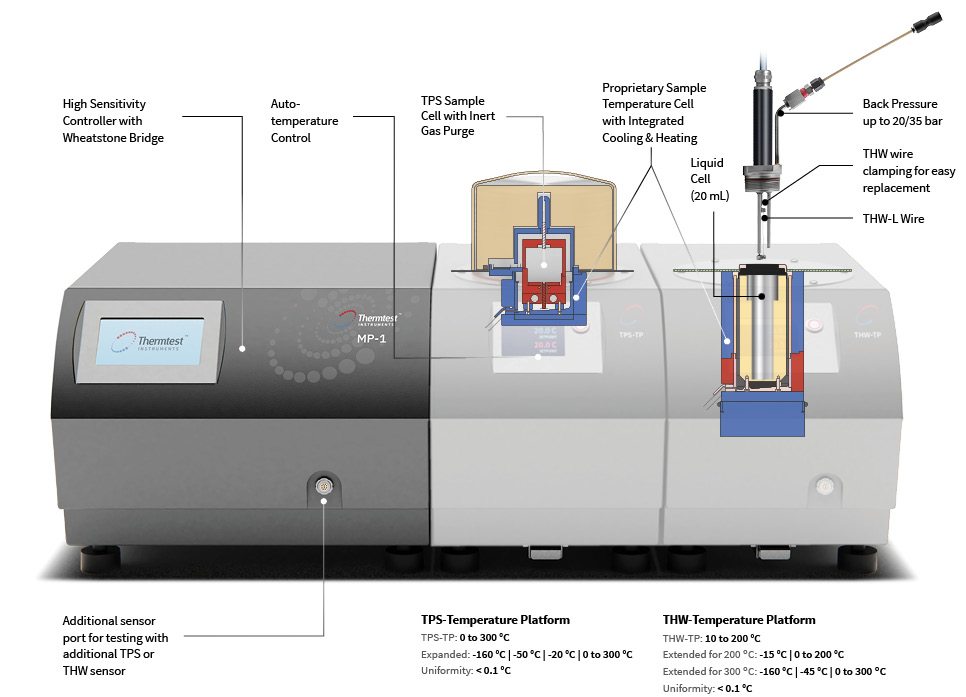
All of the transient methods share similar theory, with differences that are specific to their primary design. The basic theory is that the sensor is electrically connected to a power supply and sensing circuit. A current passes through the sensor and creates an increase in temperature, which is recorded over time. The heat generated is then diffused into the sample at a rate dependent on the thermal transport characteristics of the material.
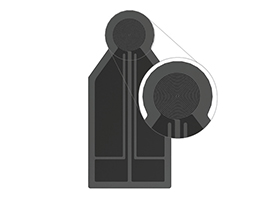
The TPS sensor designed for solids, pastes and powders is comprised of a double-spiral of nickel encapsulated between layers of insulation. Standard operation of this sensor (Two-Sided) is placed between two pieces of the same sample, with expanded use to Single-Sided sensor, which only requires one piece of sample (Single-Sided). Our proprietary TPS calculation model measures the contact resistance between sensor and sample, as well as the thermal conductivity, thermal diffusivity, volumetric specific heat and thermal effusivity of the sample.

The THW sensor designed for liquids and phase change materials (PCMs) consists of a replaceable thin heating wire (40 mm in length) secured to specially designed sensor and sample cell which allows back pressurizing liquids to measure thermal conductivity, thermal diffusivity and volumetric specific heat past boiling temperatures. Measurements are done at short test times (1 second) to limit convective effects on samples with a wide range of viscosities.

The TLS sensor designed for soil, paste and polymers consists of a thin heating wire and temperature sensor sealed in a steel tube. The sensor is completely inserted into the sample to be tested. Heat is delivered to the sample using a constant current source (q) and the temperature rise is recorded over a defined period of time. The slope (a) from plot of temperature rise versus logarithm of adjusted time is used in the calculation of thermal conductivity (k).
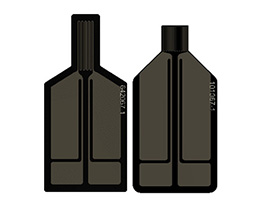
The THS sensor designed for solids is comprised of a nickel pattern encapsulated between layers of insulation. Standard operation of this sensor (Two-Sided) is placed between two pieces of the same sample with expanded use to Single-Sided sensor, which only requires one piece of sample (Single-Sided). Our proprietary TPS calculation model measures the contact resistance between sensor and sample, as well as the thermal conductivity, thermal diffusivity, volumetric specific heat and thermal effusivity of the sample.
Standard double-spiral nickel sensor patterns can be insulated in various insulation types for use at a wide range of temperatures.
Sensors for testing solids, paste, and powders. Configurations of symmetric (two-sided) with one sample piece on top and bottom of sensor and asymmetric (single-sided) requiring only one piece of sample.
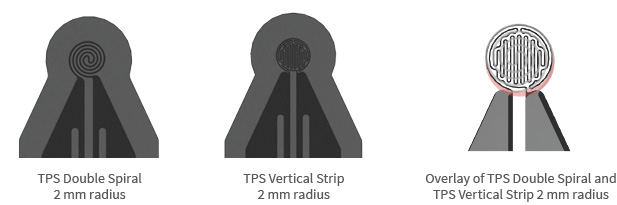
New proprietary sensor (TPS Vertical Strip) design is a near perfect circle, which better follows the ideal TPS theory. When testing with small sensor radii, this improved design reduces required corrections, while decreasing measurement uncertainty. When comparing the Corrected Radius between small diameter TPS sensors, the TPS Vertical Strip (2 mm, 1.30%) requires less correction when compared to TPS Double Spiral (2 mm, 5.75%) of the same radius. As the TPS sensor radius increases, this advantage is reduced.
| Radius (mm) | Corrected Radius (mm) | % Difference | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TPS Vertical Strip Sensor | 2 | 2.026 | 1.30 |
| 3.2 | 3.201 | 0.03 | |
| 6.4 | 6.405 | 0.08 | |
| TPS Double Spiral Sensor | 2 | 2.115 | 5.75 |
| 3.2 | 3.28 | 2.50 | |
| 6.4 | 6.591 | 2.98 | |
| 9.9 | 10.11 | 2.12 |
| Methods | TPS | THW | MTPS | THS | TLS |
| Materials | Solids, Pastes, and Powders | Liquids and PCMs | Solids, pastes, and powders | Solid rectangles | Soil, pastes, and polymers |
| Testing modules | 3-D: Bulk, Anisotropic, Slab Anisotropic, Slab, Finite, Thin-Film | 1-D: Standard, 1-D Slab, TR Thin-Films, TR Contact Resistance | General: Specific Heat |
Bulk | 3-D: Bulk, Anisotropic, Slab Anisotropic, Slab | 1-D: Standard, 1-D Slab |
Bulk, Anisotropic, Slab | Bulk |
| Thermal conductivity (W/m•K) | 0.005 to 2000 | 0.01 to 2 | 0.03 to 500 | 0.1 to 500 | 0.1 to 8 |
| Thermal diffusivity (mm²/sec) | 0.01 to 1200 | Up to 0.5 | 0.01 to 300 | Up to 300 | N/A |
| Specific heat (J/kg-K) | Up to 5 | Up to 5 | Up to 5 | Up to 5 | N/A |
| Thermal effusivity (W√s/m²K) | 5 to 60000 | N/A | 20 to 40000 | 20 to 40000 | N/A |
| Sensor contact resistance (m²K/W) | Measured | N/A | Measured | N/A | N/A |
| Sample size (mm | mL)* | 5 diameter or square | 20 mL | 25 diameter or square | 30 x 10 | 50 diameter |
| Sample thickness (mm)* | 0.01 | N/A | 0.1 | 0.1 | 100 length |
| Largest sample size (mm) | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited |
| Test time (seconds) | 0.25 to 2560 | 1 | 0.25 to 2560 | 0.25 to 2560 | 180 |
| Accuracy (Thermal conductivity) | 3% | 2% | 5% | 5% | 5% |
| Repeatability (Thermal conductivity) | 1% | 1% | 2% | 2% | 2% | Temperature range (°C)** | 0 to 300 -160 | -45 to 300 up to 750 / 1000 |
10 to 200 -40 to 200 -160 | -40 | 0 to 300 |
0 to 100 | -50 to 200 | -75 to 300 | -40 to 100 |
| Sample configuration | Symmetric (Two-Sided) | Asymmetric (Single-Sided) | Inserted | Asymmetric (Single-Sided) | Symmetric (Two-Sided) | Asymmetric (Single-Sided) | Inserted |
| Standard | ISO 22007-2:2022, ISO 22007-7:2023, GB/T 32064-2015 |
ASTM D7896-19 | ISO 22007-7:2023 | ASTM D5334-22a, ASTM D5930-17, IEEE 442-2017 |
* Based on testing module used.
** For temperature, external control required.
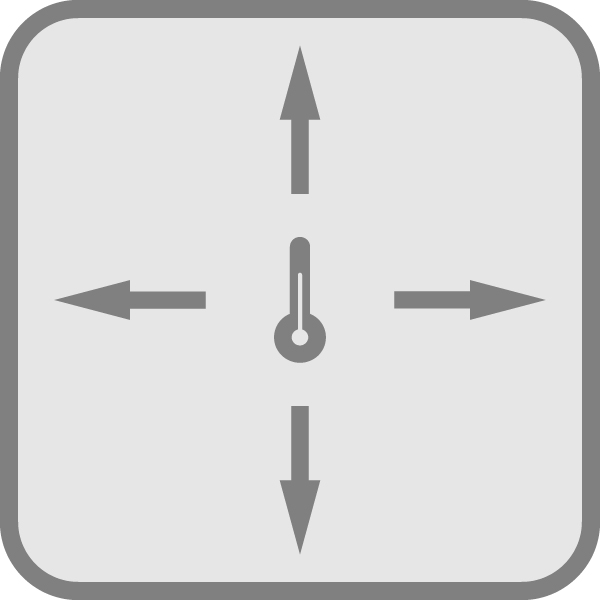
Bulk thermal conductivity, thermal diffusivity, specific heat and thermal effusivity. Symmetric and Asymmetric.
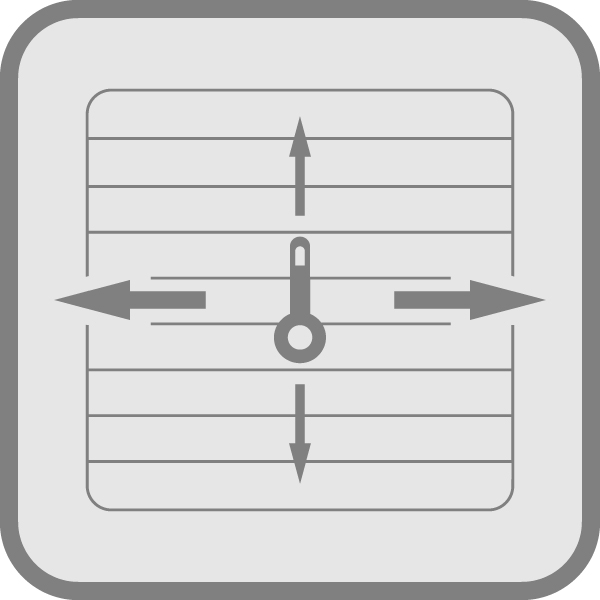
Anisotropic In-plane and out-of-plane thermal conductivity and thermal diffusivity. Symmetric and Asymmetric.
Isolated in-plane, for thermal conductivity, thermal diffusivity and volumetric specific. Symmetric and Asymmetric.

Thermal conductivity of thin-films and coatings according to ISO 22007-2.

Isolated out-of-plane, for thermal conductivity, thermal diffusivity and volumetric specific heat for elongated shapes, rods and bars. No input of volumetric specific heat is required. Symmetric and Asymmetric.

Thermal Resistance and thermal conductivity of free standing thin-films, adhesives and coatings.

Thermal Contact Resistance between two objects, similar or dissimilar objects, including effects of surface finish, pressure and temperature.

High accuracy direct measurement of specific heat. Various cell dimensions available, for improved accuracy of heterogenous materials.
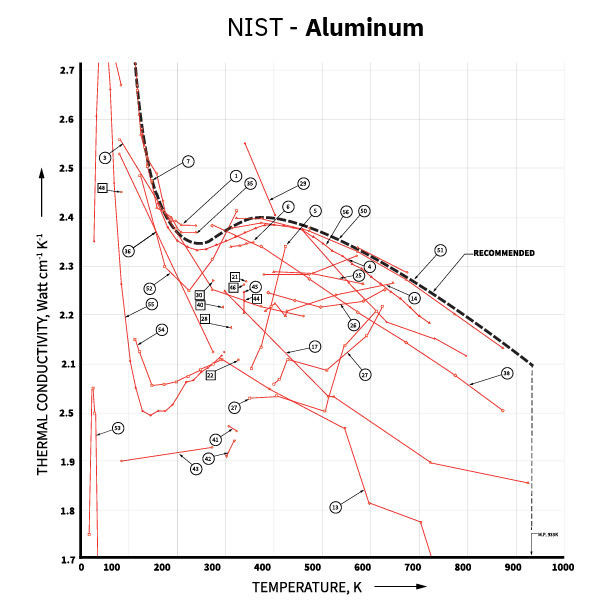
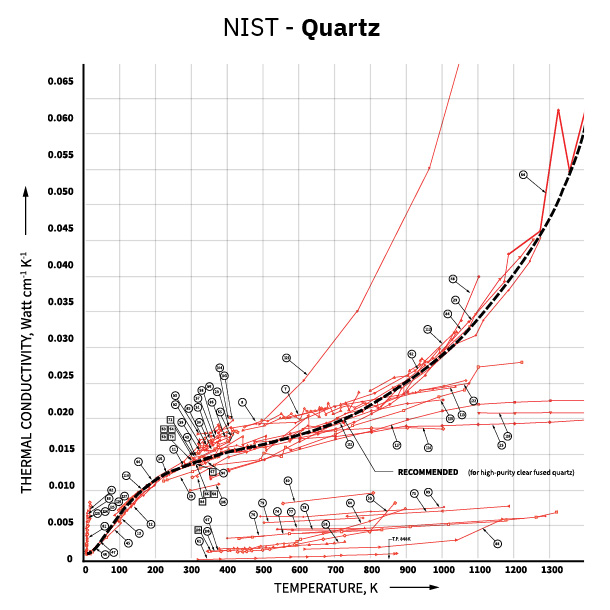
As materials are unique, the reliance on reference information to predict thermal conductivity or its relationship with temperature, can lead to the use of inaccurate data. Using NIST’s “Thermal Conductivity of Selected Materials” reference for aluminum and quartz, we can see that there is a wide variance in thermal conductivity vs. temperature. Due to the dramatic variance in global material sources, it is critically important to fully characterize materials for thermophysical properties. Optional temperature capability can be added to the MP-1, allowing for full temperature characterization.
Citation: Powell, R.W., Ho, C.Y., and Liley, P.E. (1996). Thermal Conductivity of Selected Materials. Washington, U.S.: Dept. of Commerce, National Bureau of Standards; for sale by the Superintendent of Documents, U.S.. Govt. Printing Office. pp. 17, 99.
Designed from the ground up, the MP-1 Data Acquisition Software (DAQ) smartly controls all aspects of testing and scheduling. Testing methods and experimental parameters may be selected for automated scheduling.
A unique feature for the MP-1 is the integration of a four channel switch which is designed to allow automation of multiple devices and sensors to be controlled at the same time, greatly increasing testing capacity.
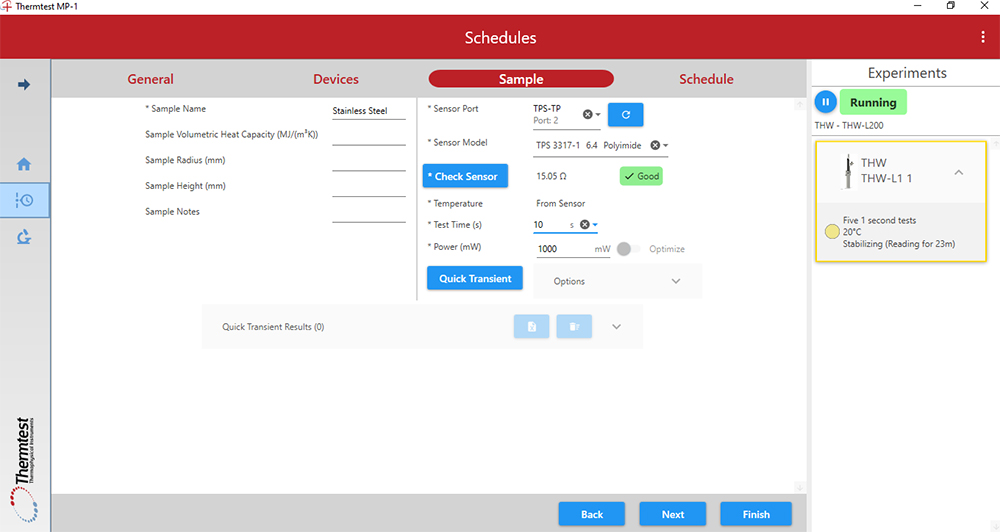
Methods and testing modules can be selected and parameters optimized for solids, liquids, pastes, and powders.
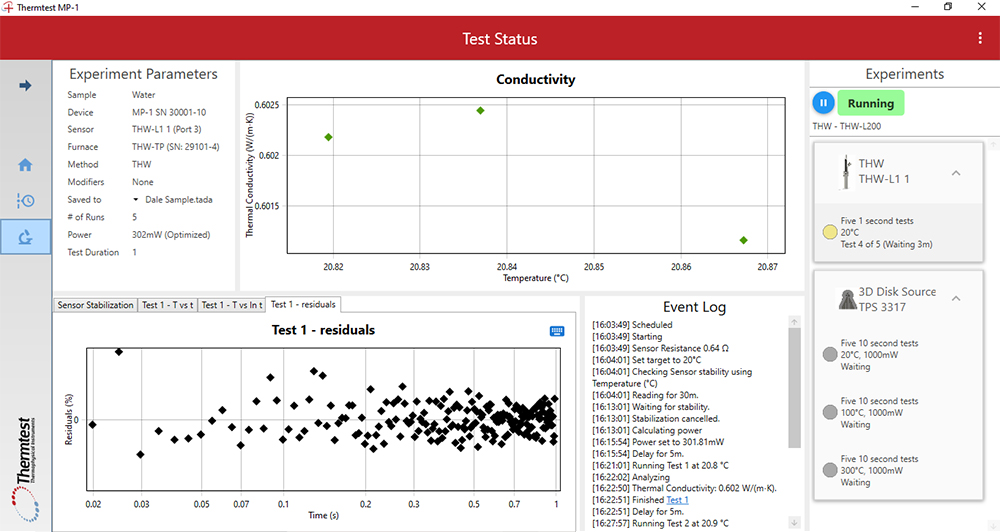
Any combination of methods, devices and sensors can be scheduled to operate at a variety of conditions, such as temperature range.
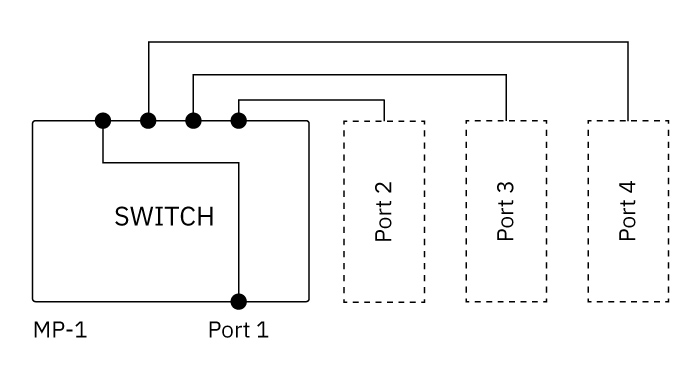
Integrated into each MP-1, the four port switch enables use of a number of optional devices, temperature platforms and sensors to maximize convenience and capacity.
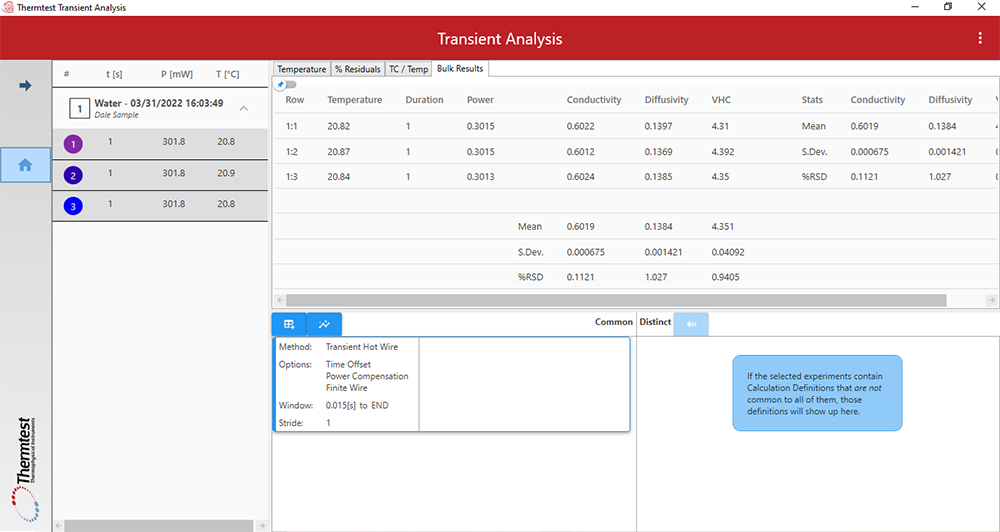
Creating a better user experience, the Analysis Software (AS) was designed to operate independent of the DAQ. A wide range of analysis operations can be conveniently accomplished. Testing data is grouped together based on method used, making corresponding calculations easy to apply.
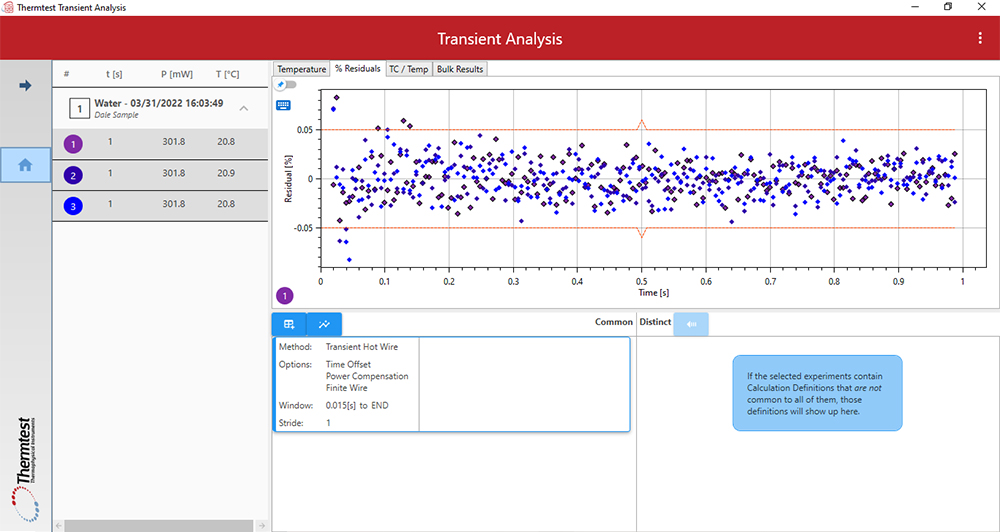
In addition to summary of results, variations in applied corrections are stored for easy comparison and exporting.
TPS theory states that the non-linear section of temperature rise vs time, known as contact resistance has to be removed, so the intrinsic thermophysical calculations are based on the linear region of transient. This can be done manually by iteratively removing start points till best fit is achieved. Although this is a suitable approach, it does take an experienced user to reduce errors and achieve required repeatability.
The contact resistance between the sensor and sample is dependent on the quality of the sample surface. When manually removing the contact resistance a small number of points (step 1) is removed and newly calculated for best fit analysis. If the resulting residual mean deviation can be improved, more points (step 2) can be removed and calculation steps repeated.
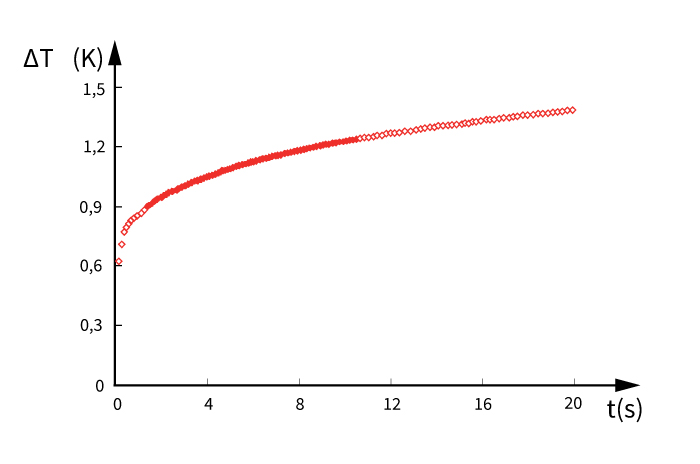
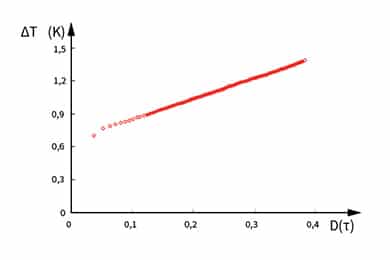
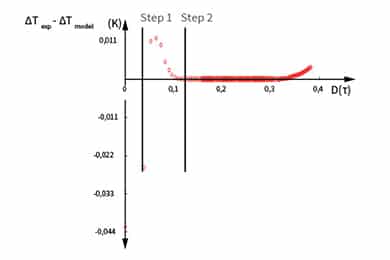
Alternatively, using our proprietary Contact Analysis (CA), the MP-1 is able to calculate the contact resistance (m²K/W) between sensor and sample, automatically removing the corresponding start time. In addition to better understanding the effects of surface finish on your measurements, this greatly simplifies the analysis for the intrinsic thermophysical properties.
Demonstrating the application of the contact analysis measurement, four samples of stainless steel 316 with different surfaces were measured for thermophysical properties. As the MP-1 is able to measure contact resistance, selection of the calculation window is greatly simplified, maximizing repeatability of the intrinsic properties of the sample as the surface roughness increases, the measured contact resistance also increases.
| Stainless Steel 316 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface Finishes | Surface Roughness Ra (um) |
Contact Resistance (m²K/W) |
Conductivity (W/m·K) |
Diffusivity (mm²/s) |
Volumetric Specific Heat (MJ/m³K) |
Effusivity (W√s/m²K) |
|
| Polished | 0.101 | Mean | 1.00E-04 | 13.80 | 3.73 | 3.70 | 7149 |
| %RSD | 6 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.2 | ||
| Machined | 0.324 | Mean | 1.54E-04 | 13.93 | 3.75 | 3.71 | 7194 |
| %RSD | 1 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.1 | ||
| 400 grit | 0.516 | Mean | 1.32E-04 | 13.84 | 3.74 | 3.71 | 7163 |
| %RSD | 2 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.1 | ||
| 80 grit | 2.78 | Mean | 2.41E-04 | 13.85 | 3.73 | 3.71 | 7171 |
| %RSD | 1 | 0.02 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | ||

Combining the special measurement features of the transient plane source (MP-1 TPS) method, the TPS Battery Package is designed to accurately measure the directional (Anisotropic) thermal conductivity, thermal diffusivity and specific heat of cylinder and pouch type batteries. The TPS Battery Package includes the required testing modules; Specific Heat Module, 1-Dimensional and Anisotropic.
Cylinder type batteries consist of sheets of anodes, separators and cathodes that are rolled into a cylinder shape and packed into a can. The round shape maximizes strength and stability, making it one of the most popular batteries manufactured.
Specific Heat Capacity is measured with TPS Specific Heat Module with Cp Cell designed for cylinder shapes. First a reference measurement is done on empty Cp cell, followed by measurement with inserted battery. Results are measured in Heat Capacity (J/K), Specific Heat (kJ/kg-K) and Volumetric Specific Heat (MJ/m³K).
Included with the Specific Module for batteries is one standard cylinder Cp Cell, TPS Sensor and Battery Insulation Block. Custom Cp Cells can also be developed for a wide range of battery sizes.
The Thermal Conductivity and Thermal Diffusivity are measured along the height of a cylinder with the 1-Dimensional (1-D) Module.
TPS Sensor of similar diameter is set-up in single-sided (asymmetric) configuration. Using the Battery Insulation Block, the battery is insulated to guard against lateral heat loss.
Included with the 1-D Module for batteries is one TPS Sensor and Battery Insulation Block. Custom TPS diameter can also be developed for a wide range of battery sizes.
The Thermal Conductivity and Thermal Conductivity are measured along the axial and radial directions.
TPS sensor is set-up in single-sided (asymmetric) configuration. The Battery Insulation Block provides known backing insulation for single-sided (asymmetric) configuration.
*can be expanded 300 °C if required
Prismatic batteries consist of sheets of anodes, separators and cathodes that are rolled into a cylinder shape and packed into a cubic form. Pouch batteries have similar construction sealed in a lightweight foil
Specific Heat Capacity is measured with TPS Specific Heat Module with Cp Cell designed for Prismatic - Pouch shapes. First a reference measurement is done on empty Cp cell, followed by measurement with inserted battery. Results are measured in Heat Capacity (J/K), Specific Heat (kJ/kg-K) and Volumetric Specific Heat (MJ/m³K).
Included with the Specific Module for batteries is one standard Prismatic - Pouch Cp Cell, TPS Sensor. Custom Cp Cells can also be developed for a wide range of battery sizes.
The Thermal Conductivity and Thermal Diffusivity are measured along the height of a Prismatic - Pouch shapes with the 1-Dimensional (1-D) Module.
TPS Sensor of similar dimensions is set-up in single-sided (asymmetric) configuration.
Included with the 1-D Module for batteries is one TPS Sensor. Custom TPS diameter can also be developed for a wide range of battery sizes (up to 250 x 250 mm).
The Thermal Conductivity and Thermal Conductivity are measured along the axial and radial directions.
TPS sensor can be set-up in one of a few different configurations:
Single-sided (Asymmetric)
TPS sensor is sandwiched between prismatic – pouch battery and known insulation backing.
*can be expanded 300 °C if required
THW Sensor for liquids, pastes and small particle powders in composite for measurements at ambient pressure.

THW Sensor for liquids, pastes and small particle powders is stainless steel construction with sealed liquid cell for use of back pressure to test past boiling points.

High-Temperature THW Sensor for liquids, pastes and small particle powders is stainless steel construction with sealed liquid cell for use of back pressure to test past boiling points.

Low-Temperature THW Sensor for liquids, pastes, and small particle powders at cryogenic conditions.

Special Phase Change Materials (PCM) with easy to load access. Unique spring design allows sample expansion and contraction while ensuring sample is in constant contact with THW wire during measurement.

The THW Ambient Density Powder Cell is suitable for basic powder sample testing at ambient pressure.

THW observation sample cell is used for liquids, powder, and paste testing. The cell has convenient glass ports for observing what is happening with the sample. Typical applications are phase separation, boiling or particle settling.

THW test cell with screw-type compression system for varying the density of powder samples can also be used to ensure powders stay in contact with THW wire.
Demonstrating the accuracy of the transient hot wire method, below are thermophysical measurements of water and ethylene glycol. Low back pressure can be applied, to allow testing past boiling points.
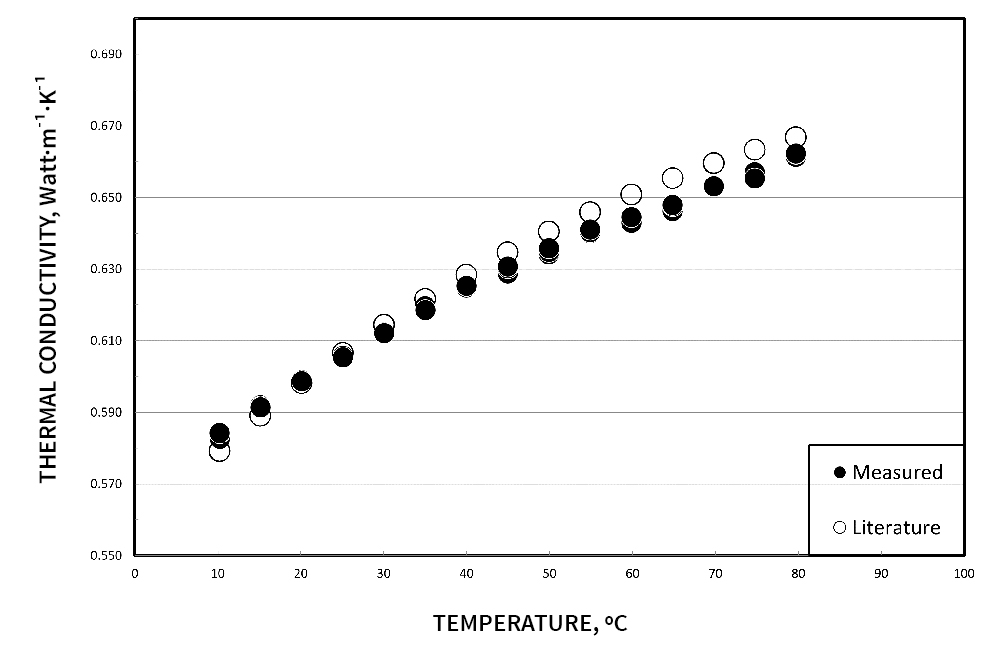
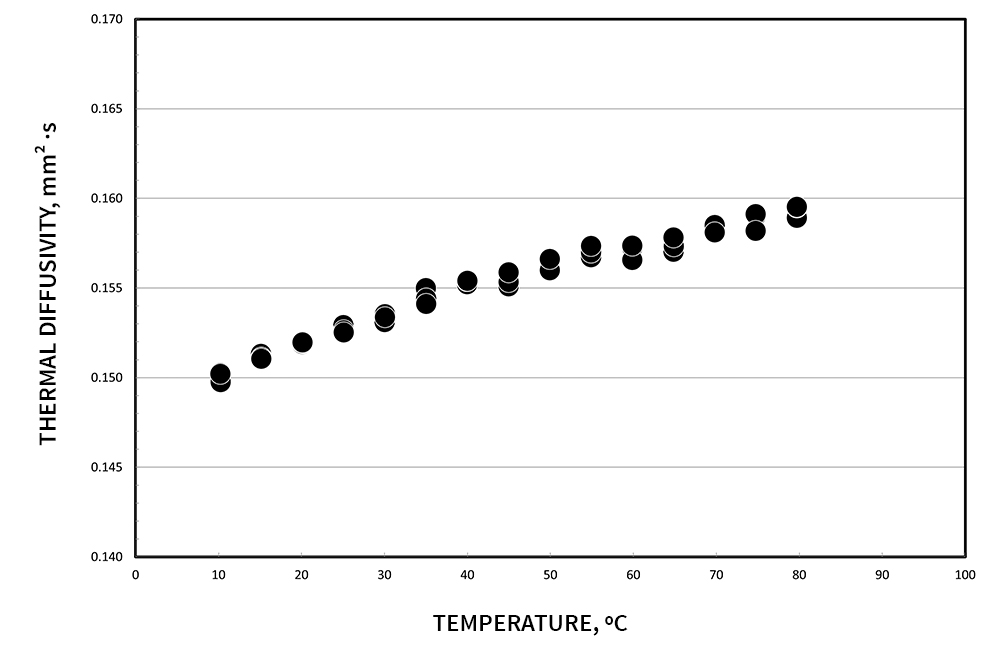
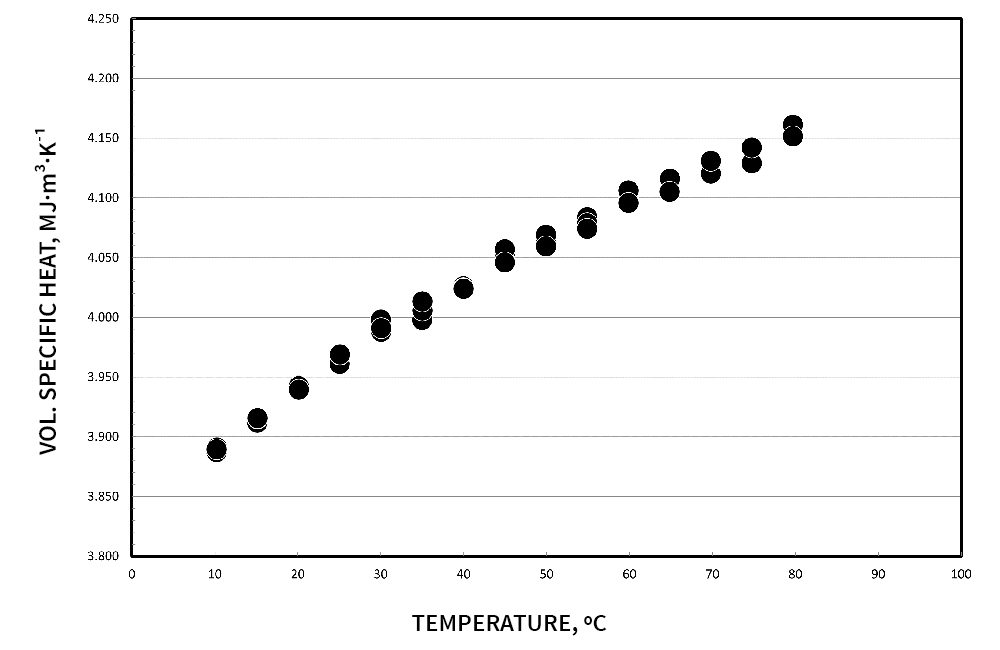
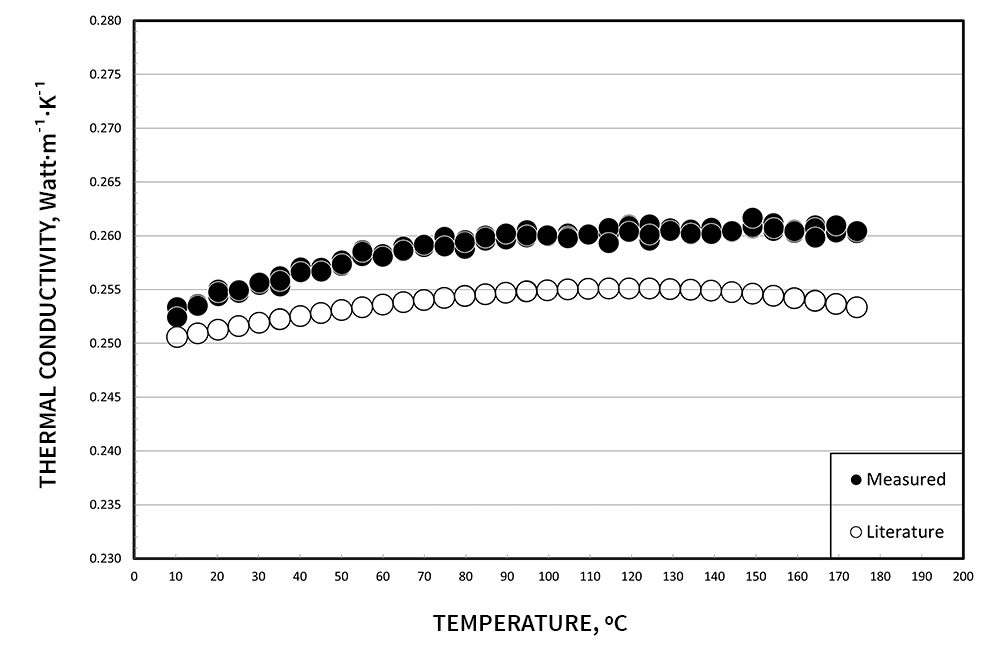
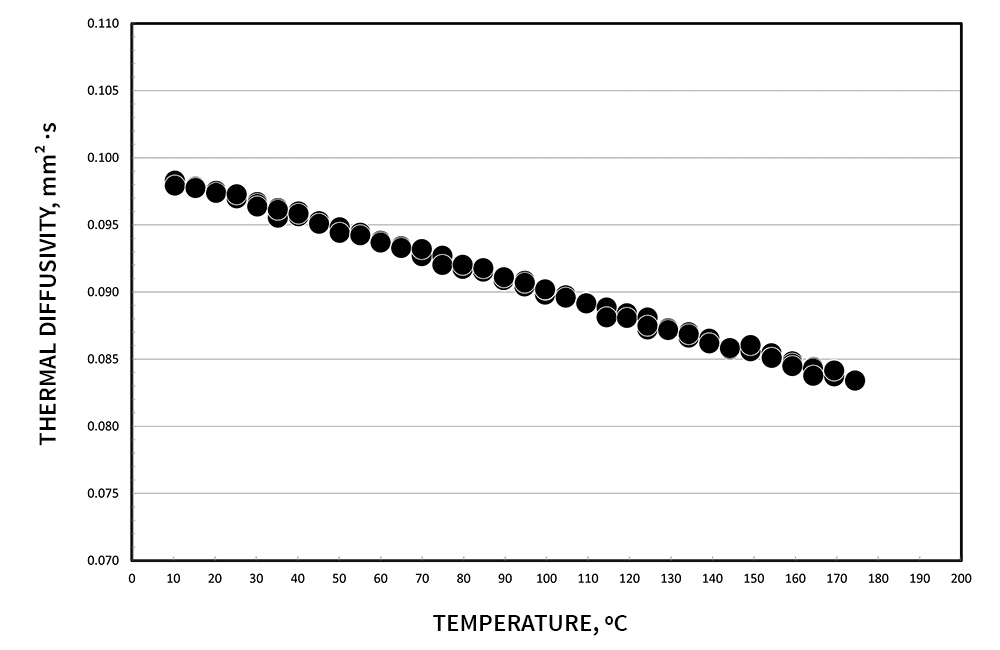
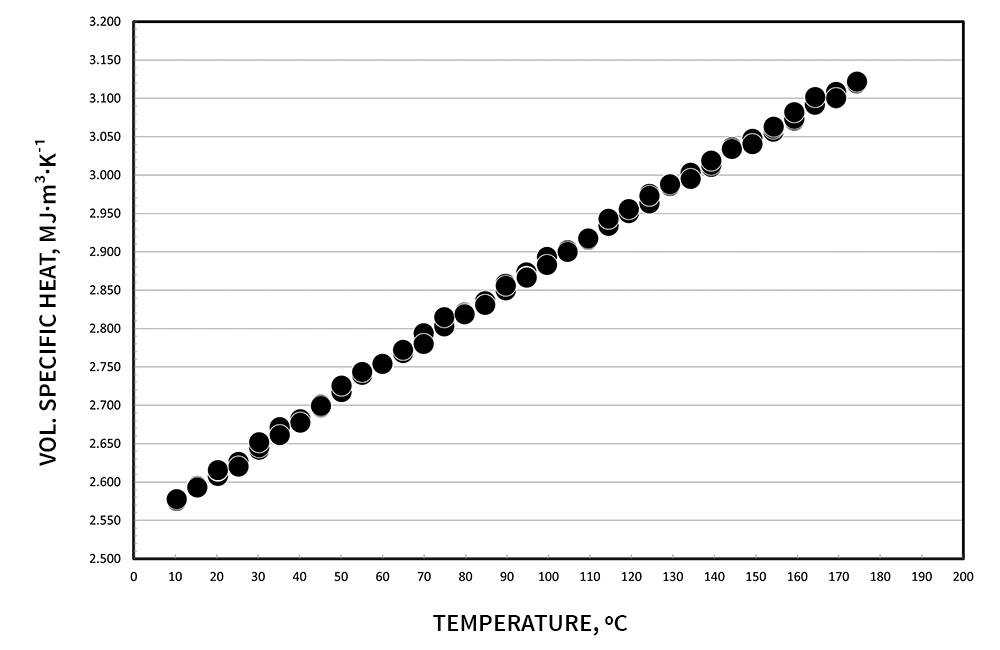
Citation: International Association for the Properties of Water and Steam, “Release on the IAPWS Formulation 2011 for the Thermal Conductivity of Ordinary Water Substance,” Sept. 2011, Plzen, Czech Republic. https://www.iapws.org/relguide/ThCond.html
Testing of phase change materials is possible with the use of the optional PCM cell. The unique spring design ensures the sample stays in contact with the sensing wire through phase changes. Isopropanol was measured for thermal conductivity, thermal diffusivity and specific heat from 20 °C to -110 °C . The sharp “anomalous” thermal conductivity rise during the phase transition is expected during the melting of the samples.
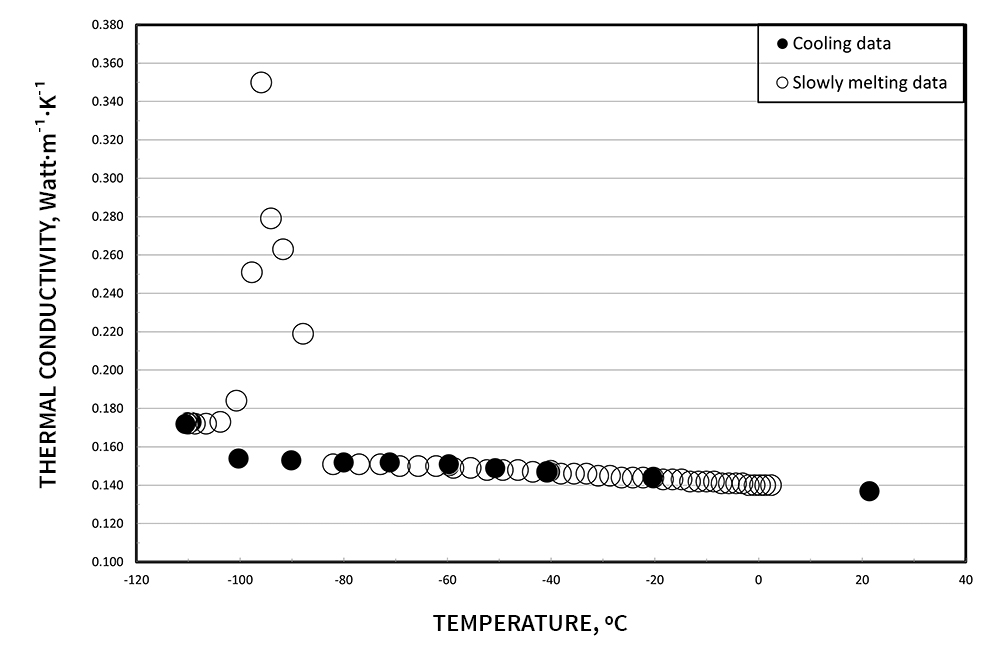
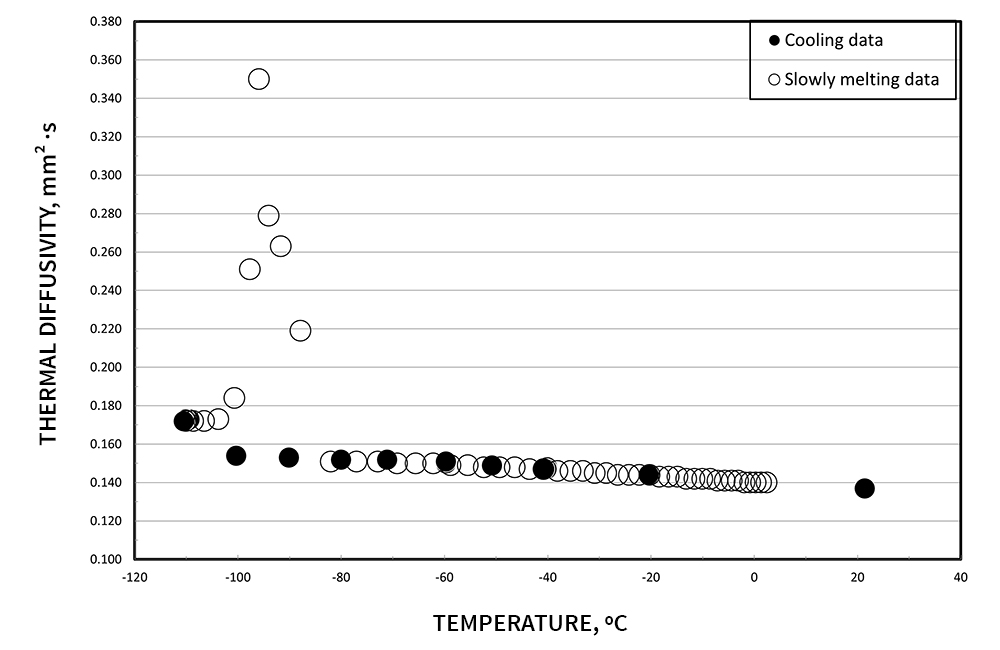

We are happy to arrange a live demonstration for you!