May 3, 2024
July 7, 2022
June 24, 2022
January 24, 2022
October 28, 2021
July 8, 2019
November 26, 2018
September 22, 2017
June 9, 2017
September 27, 2017
July 24, 2017
September 22, 2017
September 27, 2017
November 26, 2018
January 30, 2019
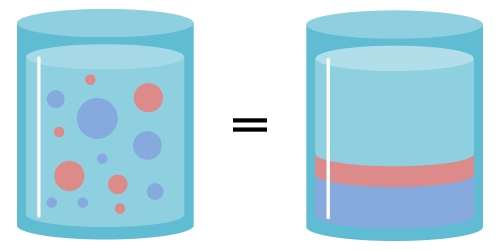
The mass of each individual component is equivalent to the total mass of the mixture, which can theoretically be broken down into separate parts.
Heat capacity is a measurable physical quantity equal to the ratio of the heat added to (or removed from) an object to the resulting temperature change. Specific heat is the amount of heat per unit mass required to raise the temperature by one degree Celsius. The heat capacity of a mixture can be calculated using the rule of mixtures.
The new heat capacity depends on the proportion of each component, which can be calculated from mass or volume. Using the mass and specific heat capacity of each component, the Rule of Mixtures Calculator calculates the specific heat capacity of the entire sample. If mass is used for one component, it must be used for all components, similarly for volume. The units of mass or volume don’t matter, as long as they match; eg: if ml are used for one component, they must be used for all components.
\[C_{p\,mixture}=\Big(\frac{m_{1}}{m_{mixture}}\Big)C_{p\,1}+\Big(\frac{m_{2}}{m_{mixture}}\Big)C_{p\,2}\]
Where:
\(C_{p}\) = Heat Capacity
\(m\) = Mass
\(m_{mixture}\) is \(m_{1}+m_{2}\)
Want to learn more about the rule of mixtures and specific heat capacity? Check out the RULE OF MIXTURES CALCULATOR blog post to learn how it works along with practical examples.
To start, input the number of materials you’d like to mix, select either volume or mass, then select your units.
Click “Continue” to go to the next step.