May 3, 2024
July 7, 2022
June 24, 2022
January 24, 2022
October 28, 2021
July 8, 2019
November 26, 2018
September 22, 2017
June 9, 2017
September 27, 2017
July 24, 2017
September 22, 2017
September 27, 2017
November 26, 2018
January 30, 2019
How to calculate thermal resistance? The thermal resistance of a whole object (like a wall) can be calculated from the resistance of each individual layer. Choose however many layers your object has, then fill out the table with each layer’s thickness, area, and resistance. You can use the material database to find the values of specific materials. All layers should have the same area, but they can have different thicknesses. Units of the calculated thermal resistance are Kelvins per Watt (K/W), and the inputs should be in meters (m), meters squares (m²) and meters Kelvin per Watt (mK/W).
Thermal Resistance:
\[ R = x / (A \ast k) \] Where:
\( R \) = thermal resistance
\( x \) = penetration depth or width of material
\( A \) = area
\( k \) = thermal conductivity
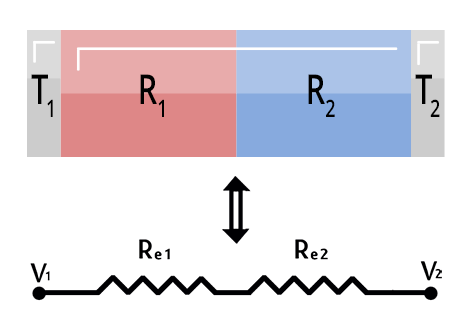
Want to learn more about thermal resistance in series calculator? Check out our blog post to learn how it works.
First input a value indicating the number of materials, and the area of the materials.
Then click “Continue” to go to the next step of the process.