May 3, 2024
July 7, 2022
June 24, 2022
January 24, 2022
October 28, 2021
July 8, 2019
November 26, 2018
September 22, 2017
June 9, 2017
September 27, 2017
July 24, 2017
September 22, 2017
September 27, 2017
November 26, 2018
January 30, 2019
Heat flux is described as the amount of energy (in joules) which passes a through a given surface over some unit of time. Heat flux is usually calculated in Watts per meter squared and can be calculated using the product of the thermal conductivity constant of aluminum and the temperature difference over the length of a sample of aluminum. This experiment will use the Heat flux through an aluminum rod to then determine the length of an aluminum rod with an unknown length.
Using the heat flux of an aluminum rod of known length, a prediction can be made of the length of another aluminum rod of unknown length.
Heat flux equation: Q = [k⋅(T1-T2)]/Δx
Rearranged for Δx: Δx = [A⋅k⋅(T1-T2)]/q
Unless otherwise stated, all of the stated materials may be found on Amazon. The total cost will be around $100
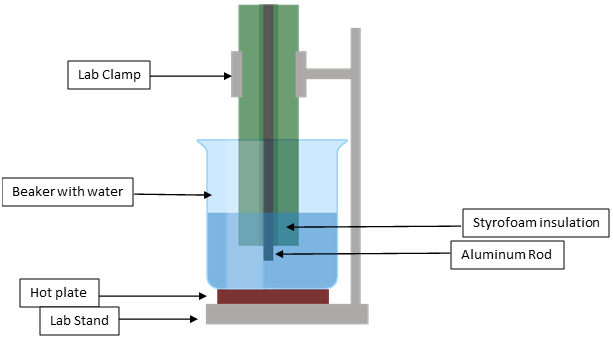
For the Heat flux to be considered the same for both rods, the exact same procedure must be followed. Leaving the rod in the hot water bath for longer than the other rod will decrease the Heat flux via an increased T2. The same is also true for the opposite, should the one rod be left in the hot water bath for a shorter period, the T2 will be smaller and thus the Heat flux greater. A substitute for Styrofoam may be used in this experiment; however, an insulator with similar properties should be used to prevent heat loss from the aluminum rod and skew the T2.
The equation employed in this experiment work under the assumption that the system is defined as steady state. Therefore, on small scale (rods smaller than ~30 cm and differing less than ~10 cm) the calculations will hold. More precise instrumentation should be used if larger scale experiments were to be performed.
Heat flux is a measure of energy passing through an area over a given time regardless of the length of that material. Should the length of a rod increase in length, the temperature at the end of that material will decrease and vice versa if exposed to the same amount of heat.
For further information on heat flux and thermal conductivity constants of other materials visit: