
January 27, 2025
Thermal energy storage (TES) is crucial since renewable energy resources have become the backbone of the world, still a constant problem of effectively storing this energy for future use remains. TES is a process to save heat energy for later use, making energy systems more efficient and flexible. From saving heat from a solar power plant to keeping extra energy from wind turbines, TES helps balance the gaps in energy supply.
Nowadays, thermal energy storage is an important part of modern systems for storing renewable energy, aiding in storing excess solar, wind and other sustainable energy sources. A major aspect of TES is thermal conductivity, which is important to understand how well heat can move. This blog helps you familiarize yourself with how thermal storage methods work better and how thermal conductivity makes these systems more efficient.
Thermal storage systems work by taking in, storing and giving out heat energy as and when needed. However, how well these systems perform largely depends on the material’s ability to move heat, where thermal conductivity comes into play. It measures the material’s ability to transfer heat, therefore when choosing what materials to use for these systems it’s important to consider these measures because it affects how fast and effectively energy can be stored and taken out.
TES system and thermal conductivity are closely tied to each other. Materials with high conductivity enable a quicker heat transfer, which means energy can be stored and retrieved more efficiently. On the other hand, materials with poor heat transfer abilities might slow down energy transfers, lowering the system’s overall efficiency.
Various aspects of TES systems depend upon thermal conductivity, such as heat loss during storage, the speed of energy release and how well a material can maintain a stable temperature. In the larger picture, choosing the right materials for the energy systems significantly impacts cost-effectiveness and reliability.
The choice of materials used in TES systems is crucial for their performance. For instance, materials like metals and certain alloys are excellent for applications that require rapid energy exchange, due to them having high thermal conductivity. Although, these options are expensive and not suitable for long-term storage applications, especially where thermal insulation is required. Which is why phase change materials are used, since they offer an excellent balance between thermal conductivity and heat storage capacity. Choosing the right material ensures that energy is stored effectively and released when needed, enhancing the overall efficiency of renewable energy storage systems.
Several methods can be used to enhance the performance of thermal energy storage systems. There are three primary categories: sensible heat storage, latent heat storage and thermo-chemical energy storage. Each of these methods offer unique advantages and has specific applications within renewable energy systems.
Sensible heat storage involves the process by which thermal energy is accumulated by an increase in the temperature of the storage medium in use such as water sand or molten salts. This is the most basic style of thermal storage, and the materials usually selected for such systems are chosen due to their specific heat and thermal conductive coefficients.
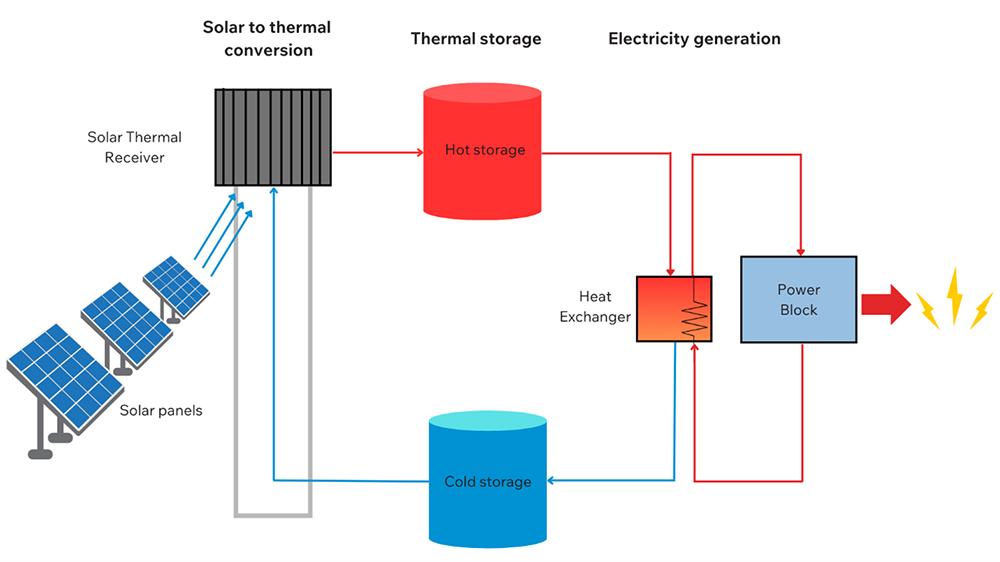
Figure 1: Two-tank thermal storage system using the molten nitrate salt
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Phase change materials like paraffins and salts are used, where large amounts of energy are released during the phase transition, such as from solid to liquid or liquid to gas. The phase transition process allows these materials to store more energy than sensible heat storage even at lower temperature differences.
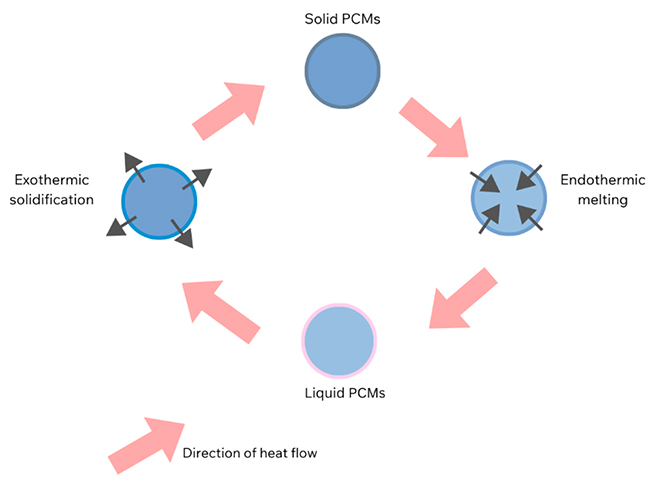
Figure 2: Process of Latent Heat storage method
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Under this method, energy is stored through endothermic and exothermic reactions (they absorb and release energy from and to their surroundings, respectively) in materials. And when the energy is needed, the chemical reaction is reversed, releasing the stored heat.
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Each of these methods has its pros and cons, therefore its use depends on the specific requirements of the energy system. However, a major factor in all these methods is the ability to transfer and store heat efficiently, showcasing the importance of thermal conductivity.
Many industries, particularly renewable energy systems, use thermal energy sources. Two main uses of TES are solar power plants and wind energy systems. These renewable resources are most often used when demand is high or when the energy source is unavailable, thus if the TES system is without an efficient storage solution, the energy generated can be wasted.
Solar Energy: Solar thermal plants use mirrors or lenses to shed sunlight onto the receiver which absorbs the heat. The heat is then transferred to a storage method using molten salts or water, using heat transfer methods. The kind of storage medium being used dictates how fast the heat can be stored and then released to produce electricity during the night.
PCMs are widely employed in solar energy systems since they can store a large amount of energy at moderate temperatures. The feature of PCMs to absorb and release heat during phase changes makes them ideal for maintaining a stable supply of thermal energy. However, the thermal conductivity of PCMs is still a concern and several researchers to overcome the problems associated with the low thermal conductivity of PCMs have proposed methods such as the addition of conductive fillers or modification of the structure of the PCM.
Wind Energy: Wind energy systems focus on converting kinetic energy into electricity. Therefore, TES systems can be used to store surplus energy generated during high wind periods. If combined with other renewable sources, like solar, thermal energy storage can provide a stable energy supply even when wind speeds are low. This is why thermal conductivity remains an important consideration in these systems, since it dictates how efficiently energy can be transferred to and from the storage medium.

Figure 3: Solar energy plants absorb and stores heat to use as thermal energy for later use
The soaring need for proper renewable energy storage has boosted creativity that helped refine TES systems as well as the thermal attributes. One of the innovations is the preparation of higher thermal conductivity composite materials for TES application. Such materials are meant to help get closer to achieving high energy density and at the same time provide efficient dissipation of heat.
Another area of innovation relates to the enhancement of phase change materials’ thermal conductivity using nanomaterials. Utilizing nanoparticles, it is possible to enhance heat transfer rate and therefore increase energy storage and releasement. This has important consequences for renewable energy systems where every improvement means a more reliable electricity supply and lower prices.
Thermal energy storage is one of the crucial technologies out of all contemporary renewable energy technologies because it offers a suitable means of capturing, storing, and subsequently releasing thermal energy. Therefore, thermal conductivity is a critical parameter that defines material choices, heat transfer rates, and system performance of these systems.
With the increasing call for renewable energy, there is also the rising requirement for efficient TES systems that deliver adequate energy storage. Through the application of thermal methods as well as the analysis of the effects of thermal conductivity, engineers and researchers can go further in the advancement of advanced TES technologies for supporting the energy transition moving towards a more sustainable world.
Hafiz Muhammad Ali, T.-u. R. (2024, January). Advances in thermal energy storage: Fundamentals and applications. Retrieved from Science Direct: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0360128523000394
Lingkun Liu, D. S. (2016). Thermal conductivity enhancement of phase change materials for thermal energy storage: A review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 1406.
Shaofei Wu, T. Y. (2020). Thermal conductivity enhancement on phase change materials for thermal energy storage: A review. Energy Storage Materials, 251-295.