
September 1, 2023
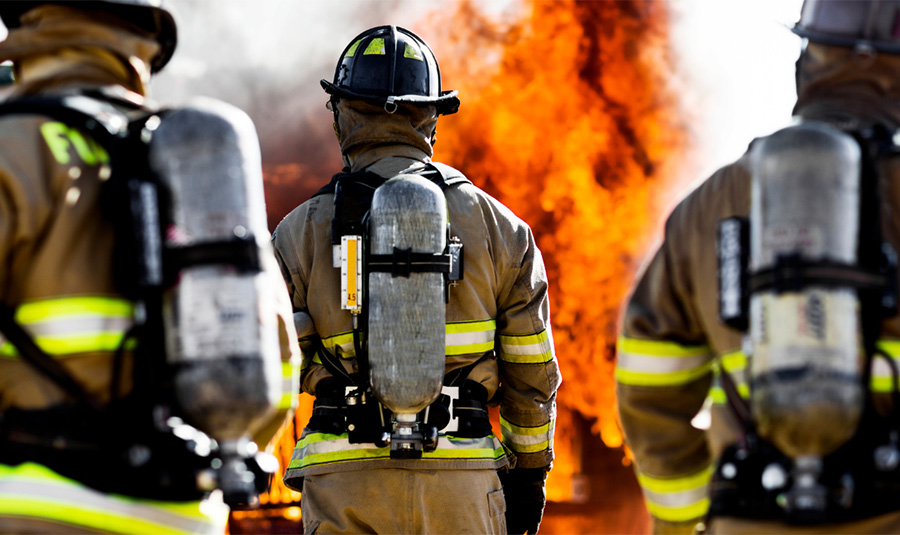
Firefighters are the unsung heroes who risk their lives to protect our communities from the devastating impact of wildfires. These brave individuals are often exposed to extreme temperatures and hazardous conditions that can result in severe injuries or even loss of life. Their attire is not just a uniform but a critical piece of safety equipment that can mean the difference between life and death. This article explores the groundbreaking advancements in heat-resistant attire designed to offer firefighters the highest level of protection against the harsh and unpredictable conditions they face in wildfires.

Figure 1. The McDougall Creek wildfire burns on the mountainside above houses in West Kelowna, British Columbia, on Friday, Aug. 18, 2023. Photo and story obtained from Darryl Dyck/The Canadian Press via The Canadian Weather Channel
Wildfires are unlike any other type of fire. They are unpredictable, fast-spreading, and can engulf large areas in minutes. Firefighters combating natural disasters face extreme temperatures exceeding 1000 degrees Fahrenheit and other hazards like falling debris and toxic smoke. Although effective for structural fires, traditional firefighting gear may not offer adequate protection in the volatile environment of a wildfire, making the need for specialized, advanced heat-resistant attire more pressing than ever.
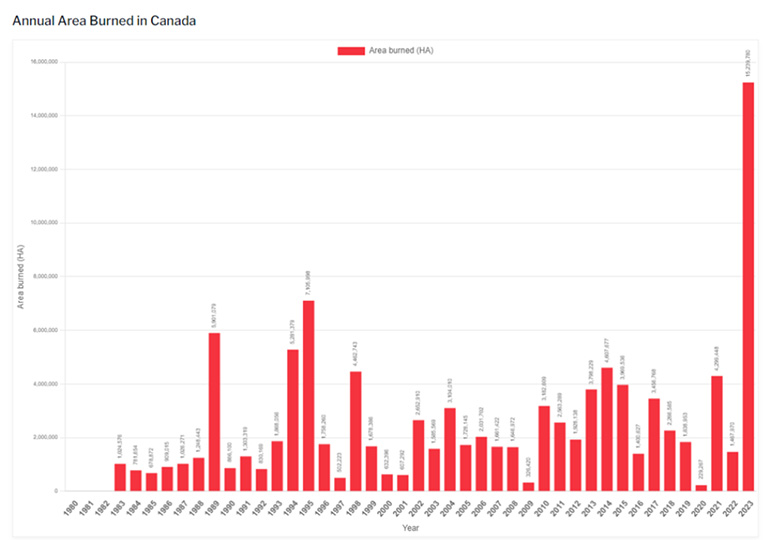
Figure 2. A graph showing the intensity of the Canadian Wildfires in 2023 from the Canadian Interagency Forest Fire Centre.
Firefighters primarily design traditional firefighting gear for structural fires, which generally have less intensity than wildfires. Such equipment often needs more specialized materials and technologies to withstand the extreme temperatures and conditions of a wildfire. This gap in protection can lead to an increased risk of heat-related illnesses, burns, and other severe injuries for firefighters.

Figure 3. A firefighter’s helmet was purposely designed to have the duckbill at the back to prevent hot debris and water falling down their backs
One of the most significant advancements in heat-resistant attire is the development of innovative textiles. Engineers have developed these materials to provide superior breathability while maintaining thermal protection. This is critical because firefighters must stay agile and comfortable during extended periods of strenuous activity. Fabrics with enhanced breathability features enable firefighters to endure prolonged periods without overheating, thus allowing them to perform their duties more effectively and safely.

Figure 4. An image depicting the various gear a firefighter wears to protect themselves.
Another area where technology has substantially impacted is the development of improved insulation technologies. Traditional firefighting gear often relies on layers of material to provide insulation, which can be cumbersome and restrict movement. Newer technologies use advanced materials that offer superior insulation with less bulk. These innovations minimize the risks associated with extended exposure to high temperatures and flames, reducing the likelihood of conduction-based burn injuries.
To learn more about the specific materials used and their ability to protect from heat, including measuring the thermal resistance, check out this article on The Materials and Mechanisms of Thermal Protective Clothing.
The implications of these advancements extend far beyond just providing better protection against heat and flames. They also profoundly impact the overall safety and well-being of firefighters. By minimizing injury rates and reducing the physical strain associated with wearing heavy, cumbersome gear, these developments significantly improve the overall effectiveness of emergency response teams, leading to quicker containment of wildfires and reducing their devastating impact on communities and ecosystems.
Advanced heat-resistant attire also contributes to operational efficiency. The enhanced comfort and mobility allow firefighters to move more freely and focus on their tasks rather than being hindered by their gear. This can lead to quicker decision-making and more effective firefighting strategies, ultimately saving more lives and property. Which, given the current state of the Canadian Wildfire situation, is necessary.
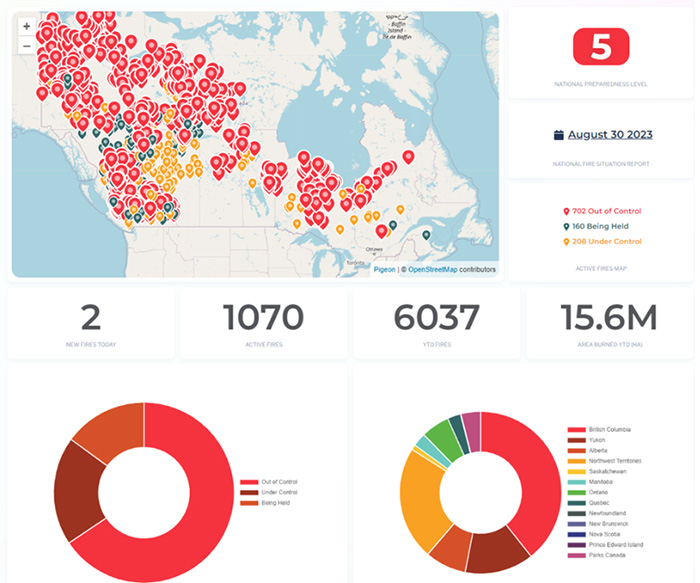
Figure 5. The information above was secured from the Canadian Interagency Forest Fire Centre Inc., on August 31, 2023.
Although the advantages of advanced heat-resistant attire are evident, some argue that the expenses related to implementing these high-tech materials and conducting extensive research and development may surpass the benefits. Fire departments could utilize their limited resources better by investing in training programs or acquiring new firefighting equipment.
Another point of contention is the current regulations governing the testing procedures for heat-resistant attire. Critics argue that existing standards may need to be more stringent to ensure the highest level of safety. Stricter standards and rigorous testing protocols provide a more reliable framework for evaluating the effectiveness of new technologies and materials.
Developing effective heat-resistant attire for firefighters is paramount in ensuring their safety. While debates around costs and regulatory standards are valid, they should not hinder ongoing efforts to advance technology and scientific research. In light of the more frequent and severe wildfires caused by climate change, it is crucial to continue innovating and enhancing firefighter protection garments.

Figure 6. A firefighter is able to move quicker with protective gear.
By prioritizing technological advancements and scientific insights, firefighters can face the challenges of battling wildfires with improved protection, ensuring their safety and ability to protect lives and preserve communities effectively.
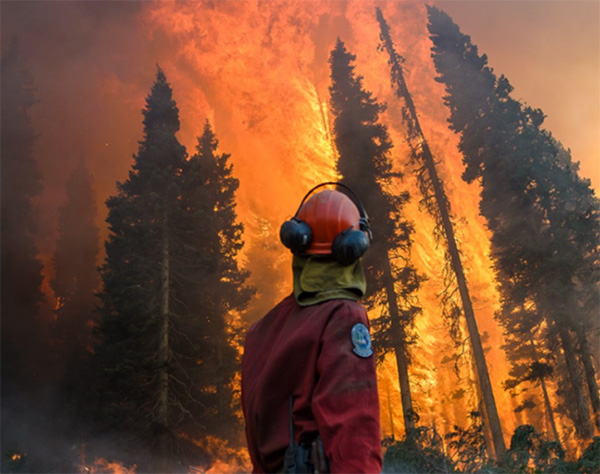

Figure 7. A firefighter staring at the intensity of the fire in British Columbia. Photo courtesy of BCGEU via Pique News Magazine.
The current wildfire situation in Canada is alarming, with fires raging across multiple provinces, including Ontario, Quebec, and British Columbia. The fires have been described as “relentless” by NASA’s Earth Observatory, and the situation shows no signs of improving any time soon. The impact of these wildfires on communities and the environment is severe, raising concerns about climate change and its destructive effects.
As a company that values innovation, precision, and a commitment to customer needs, Thermtest urges its audience to act and support those affected by the wildfires. Consider donating to the Canadian Red Cross to provide immediate relief and long-term recovery to the impacted areas.
Thermtest recognizes the urgency of the situation and encourages its readers to act swiftly. Your contribution can make a significant difference in providing critical resources to the affected communities, including food, shelter, and emotional support.
We believe in the power of supporting each other in times of urgency and difficulties. We invite our readers to join us in helping those impacted by the wildfires. Please follow the link provided to make your donation and support the Canadian communities.
Donate to the Canadian Red Cross Wildfire Relief
Lawson, L. K., Crown, E. M., Ackerman, M. Y., & Douglas Dale, J. (2004). Moisture effects in heat transfer through clothing systems for wildland firefighters. International journal of occupational safety and ergonomics, 10(3), 227-238.
Song, G., Mandal, S., & Rossi, R. (2016). Thermal protective clothing for firefighters.
Torvi, D. A., & Hadjisophocleus, G. V. (1999). Research in protective clothing for firefighters: state of the art and future directions. Fire technology, 35, 111-130
Ghazy, A., & Bergstrom, D. J. (2012). Numerical simulation of heat transfer in firefighters’ protective clothing with multiple air gaps during flash fire exposure. Numerical Heat Transfer, Part A: Applications, 61(8), 569-593.
Lu, Y., Li, J., Li, X., & Song, G. (2013). The effect of air gaps in moist protective clothing on protection from heat and flame. Journal of fire sciences, 31(2), 99-111.
Chapline, G., Rodriguez, A., Snapp, C., Pessin, M., Bauer, P., Steinetz, B., & Stevenson, C. (n.d.). Thermal Protection Systems. 18.
Clo—Clothing and Thermal Insulation. (n.d.). Retrieved August 27, 2023, from https://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/clo-clothing-thermal-insulation-d_732.html
Clothing | National Collaborating Centre for Environmental Health | NCCEH – CCSNE. (n.d.). Retrieved January 21, 2021, from https://ncceh.ca/content/clothing
Pan, N. (2019). Unique Thermal Properties of Clothing Materials. Global Challenges, 3(7), 1800082. https://doi.org/10.1002/gch2.201800082