The Measurement Platform-2 (MP-2) is an advanced meter with unique selection of transient thermal conductivity sensors for a variety of applications, with a focus on primary measurements. The transient thermal conductivity sensors share similar principles of operation.
The sensor wire is heated using a constant current source (q) and the temperature rise is recorded by monitoring the change in electrical resistance of the wire (THW and EFF) or by resistance temperature detector device (TLS). For samples of high thermal conductivity, resistance increases more slowly over time; for samples of low thermal conductivity, resistance increases more quickly over time.
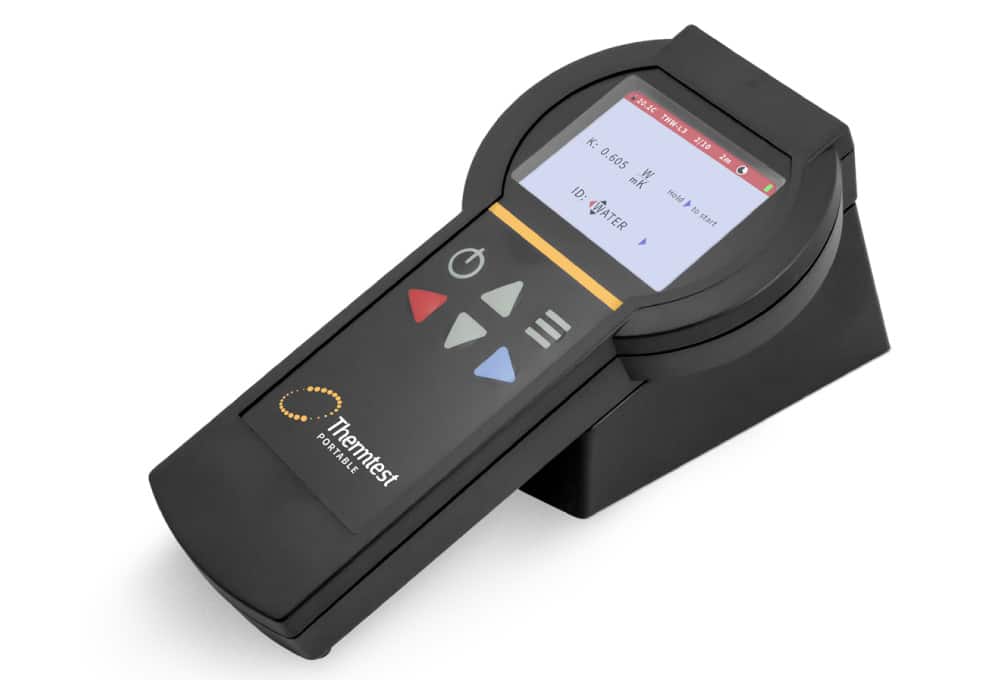

Picture 1. Thermtest MP-2 Thermal Conductivity Meter
Thermal conductivity MP-2 users benefit from the convenience and accuracy gained when using primary testing methods. The MP-2 controller auto-detects the connected sensor and loads corresponding testing parameters.
Measurements are easily performed with the smart on-board software and transferred to computer with an included Windows utility program.
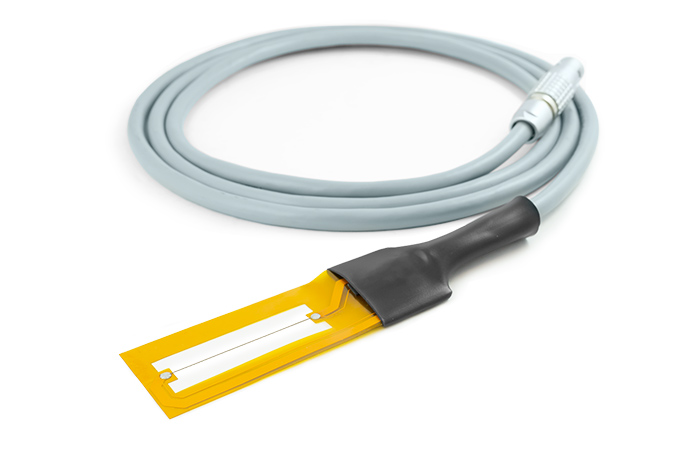

Picture 2. Thermtest THW-S sensor for use with the MP-2 portable meter.
The THW-S sensor is one of the many sensors offered with the Thermtest Portable Measurement Platform (MP-2). This sensor offers simple yet accurate measurements of insulation and soft materials from 0.01 to 2 W/m·K via the transient hot wire method. The THW-S has a 5% accuracy and a 2% reproducibility of measurement, making it a highly accurate and precise instrument for measuring the thermal conductivity of many different types of samples.
The THW-S has a detect current setting that determines the appropriate amount of current to apply based on a test measurement. By reading the result of the test measurement, a current will be set that results in an optimal temperature rise of the sample during testing.
Expanded polystyrene (EPS) and ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) are both types of foams with many commercial uses. EPS is commonly used in food-safe containers and as building insulation, while EVA is mostly known for its use in craft foams and sport equipment. Both of these foams are similarly insulative, each with an R-value around 4/inch.
The R-value is a measure of a material’s energy efficiency based on its resistance to heat flow, per unit area. The higher the R-value, the higher the insulating capability and therefore lower thermal conductivity. The thermal conductivity of a material is an intrinsic property, independent of thickness.
This application sheet uses the Thermtest THW-S sensor to measure the thermal conductivity of these two types of foam insulation. After calibration, the thermal conductivity of EPS and EVA foam can be measured with a high degree of accuracy.

Figure 1: MP-2 handheld with Thermtest THW-S sensor
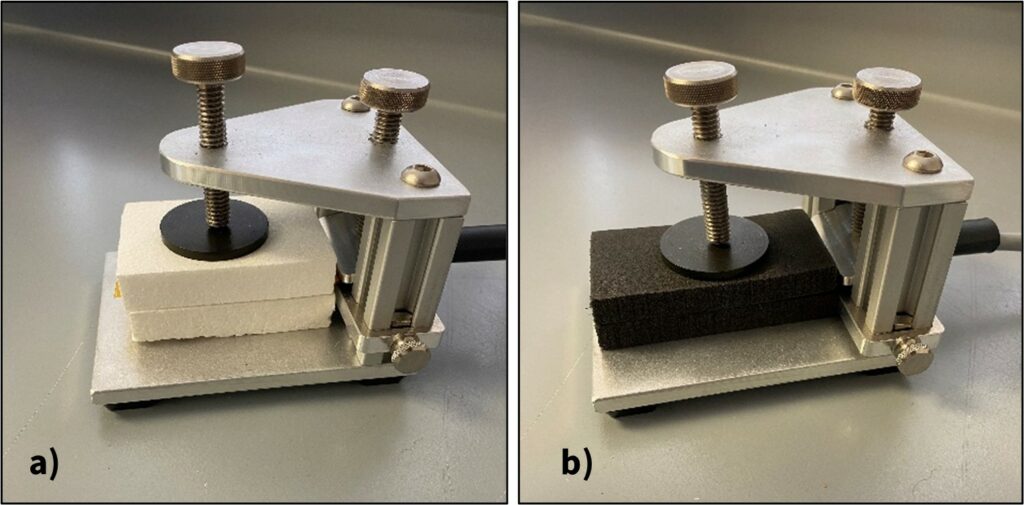
Figure 2: Set-up of the sample holder with the THW-S sensor between two pieces of a) EPS foam, b) EVA foam.
Table 1: Results of measuring EPS and EVA foam with the Thermtest THW-S sensor at room temperature.
| Sample | Average Thermal Conductivity (W/m/K) (n = 5) |
Relative Standard Deviation (%) (n = 5) |
Known Value via ISO 22007-2:2015 (W/m·K) |
Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPS Foam | 0.0335 | 0.67 | 0.0335 | 0.06 |
| EVA Foam | 0.0368 | 0.92 | 0.0366 | 0.44 |